What is Topology
The physical topology of a network refers to the configuration of cables, computers, and other peripherals. Physical topology should not be confused with logical topology which is the method used to pass information between workstations.
Type of Network Topology :
Bus Topology
- Consists of two distinct and terminated ends
- Uses 'T' connector to connect a device
- Commonly used for 10Base5 and 10Base2 networks and is seldom used toda
Advantages
- Requires less cable
Disadvantages
- Difficult to move and change
- Single cable failure brings down the entire network
- Difficult to troubleshoot
Ring Topology
- Each PC is connected directly to two other PC's
- Data Move one way
- Uses network token-passing access methods referred to as Token Ring.
Advantages
- Easy to troubleshoot
Disadvantages
- Expensive (use multiple cable)
- Single cable failure bring down the entire network
Star Topology
- PC's are connected to a central point (hub, switch, access point)
- Commonly used for 10Base-T, 100Base-TX or 1000Base-T network
Advantages
- Single cable failure won't bring the whole network down
- Easy to troubleshoot
- Scalable
Disadvantages
- Expensive (multiple cable)
- Single point of failure (hub, switch)
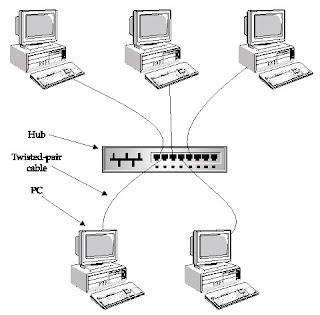 Star Topology
Star Topology
Mesh Topology
- Path from every machine to every other machine
- n hosts = n(n-1)/2 connections
- Partial mesh don't incur quite the same expense in term of cabling but, of course, lose some of the redundancy
Advantages
- High fault tolerance
Disadvantages
- Very expensive, multiple cables
Point-to-Point Topology
- Direct connection between two device
- Connections between an interface on a router to multiple destination routers






0 comments:
Post a Comment